Anomalous Upper-Ocean Circulation of the Western Equatorial Pacific following El Niño Events
Yilong Lyu, Yuanlong Li, Jianing Wang, Jing Duan, Xiaohui Tang, Chuanyu Liu, Linlin Zhang, Qiang Ma, and Fan Wang
Published in JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY, November 2020
Mooring measurements at ~140°E in the western equatorial Pacific Ocean documented greatly intensified eastward subsurface currents, which largely represent the nascent Equatorial Undercurrent, to ~67 cm s−1 in boreal summer of 2016. The eastward currents occupied the entire upper 500 m while the westward surface currents nearly disappeared. Historical in situ data observed similar variations after most El Niño events. Further analysis combining satellite and reanalysis data reveals that the eastward currents observed at ~140°E are a component of an anomalous counterclockwise circulation straddling the equator, with westward current anomalies retroflecting near the western boundary and feeding southeastward current anomalies along the New Guinea coast. A 1.5-layer reduced-gravity ocean model is able to crudely reproduce these variations, and a hierarchy of sensitivity experiments is performed to understand the underlying dynamics. The anomalous circulation is largely the delayed ocean response to equatorial wind anomalies over the central-to-eastern Pacific basin emerging in the mature stage of El Niño. Downwelling Rossby waves are generated by the reflection of equatorial Kelvin waves and easterly winds in the eastern Pacific. Upon reaching the western Pacific, the southern lobes of Rossby waves encounter the slanted New Guinea island and deflect to the equator, establishing a local sea surface height maximum and leading to the detour of westward currents flowing from the Pacific interior. Additional experiments with edited western boundary geometry confirm the importance of topography in regulating the structure of this cross-equatorial anomalous circulation.
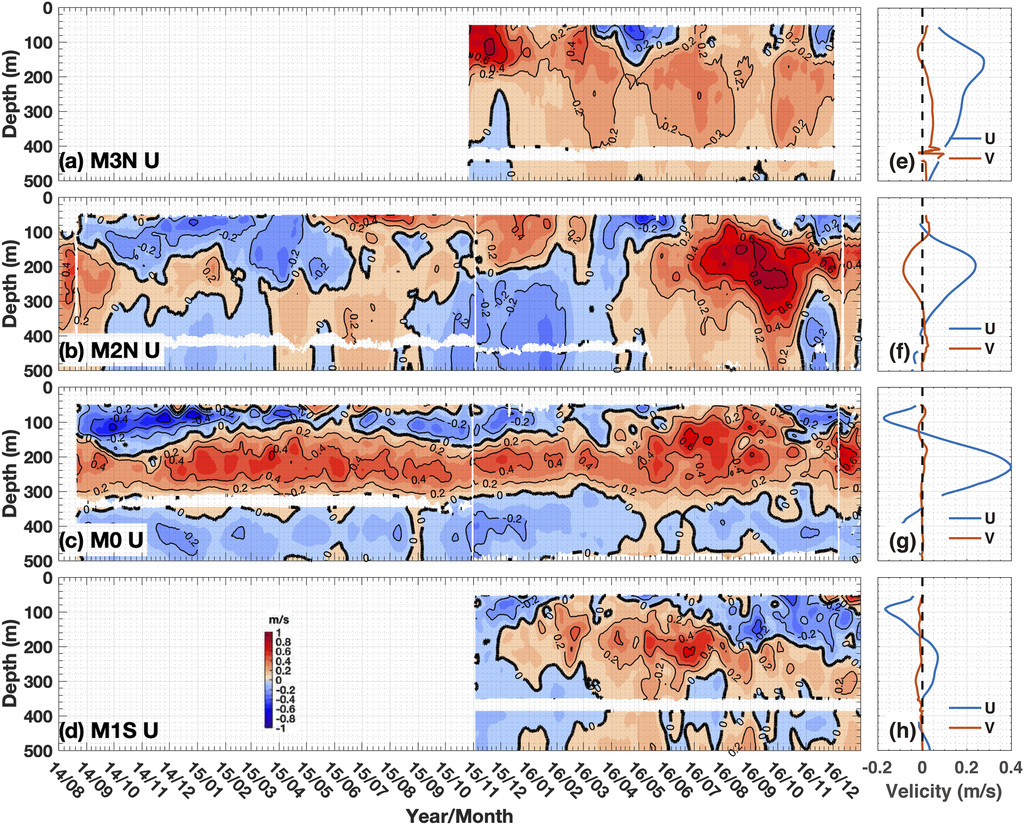
Time–depth plots of daily zonal current U (m s−1) for August 2014–December 2016 derived from the moorings of (a) M3N, (b) M2N, (c) M0, and (d) M1S; U is smoothed using a 9-day-moving-average filter. For daily data, tick marks on the x axis indicate the first day of each month (hereinafter the same). Also shown are the mean zonal (blue) and meridional (red) velocity profiles derived from the moorings of (e) M3N, (f) M2N, (g) M0, and (h) M1S.
Citation: Journal of Physical Oceanography 50, 11; 10.1175/JPO-D-20-0011.1
Lyu, Y., Li, Y., Wang, J., Duan, J., Tang, X., Liu, C., Zhang, L., Ma, Q., & Wang, F. (2020). Anomalous Upper-Ocean Circulation of the Western Equatorial Pacific following El Niño Events, Journal of Physical Oceanography, 50(11), 3353-3373. https://doi.org/10.1175/JPO-D-20-0011.1.